In recent tips, we talked about skin irritations and pressure caused when billets are not positioned correctly, the buckle is too high, or the shape of the girth restricts freedom. Does your saddle slide forward? Let’s examine correct girth alignment.
Try this experiment: take an hourglass and try to tie a string around either the top or the bottom half. The string will always migrate to the narrowest part of the hourglass – the middle, connective piece. Your horse’s girth will do the same – it will migrate automatically to the narrowest part of the horse’s thoracic area; we call this the girth area. A saddle which has been girthed up anywhere behind this area will slide forward during riding; taking the saddle and the rider with it and leaving the correct saddle support area – if it has been correctly positioned there during mounting. This natural tendency to find the ‘area of least resistance’ will cause the saddle to move forward onto the shoulder.
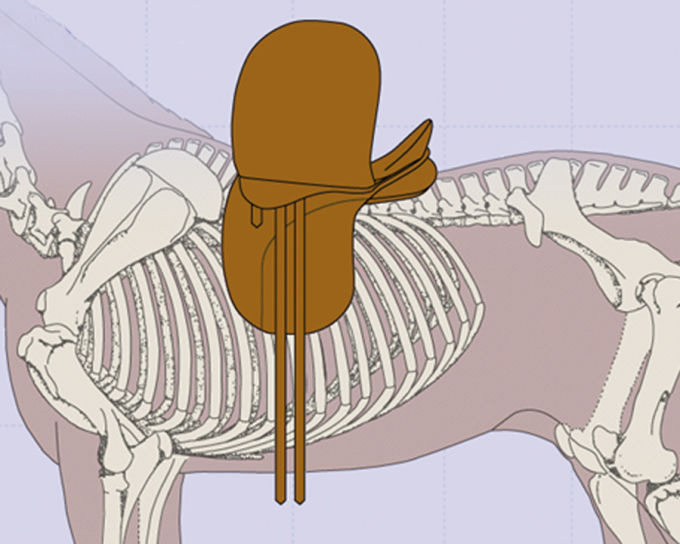


In dressage nowadays, short girths are the rule with long billets. A huge advantage here is that the girth buckles don’t bother the rider at his thighs, and usually allow the saddle to be fastened more securely. However, the girth buckles may now be located at a very sensitive area of the horse’s ribcage.

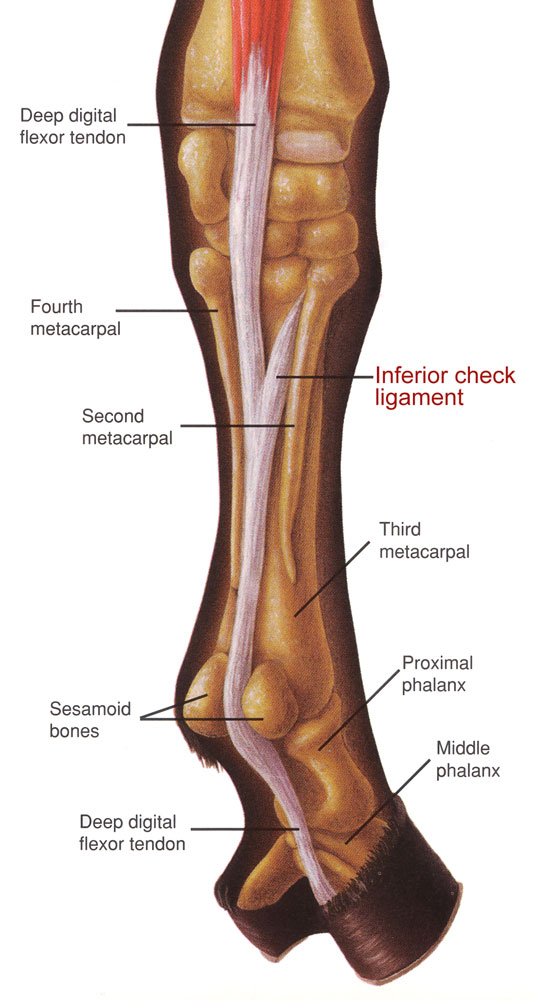
The longer girth used in jumping or eventing saddles is usually buckled on the sweat flap, which means that there is relatively thick second leather layer protecting the horse’s flank from the buckle. A short girth is buckled directly on the side of the horse, so that the buckle, which may be protected minimally with only one thin layer of leather, may cause pressure here as well. The area where the girth is positioned and buckled is an area where several muscle groups converge and have their sensitive points, which means that we should avoid irritating them if possible.
The girth should be buckled as close to the widest part of the horse’s side as possible (i.e. as high up as possible) so that the buckles are ‘pulled away’ from the ribcage and don’t put unnecessary pressure on the horse side and the insertion points of the M. Pectoralis profundus.

In the past, foregirths and point billets helped to prevent the saddle from slipping forward, or the saddle was girthed on really tightly to keep it in the correct position. Today we know however, that it is partially due to the billet position on the saddle that causes the sliding forward – and their position can be checked simply when the saddle is lying on the horses back and seeing where the billets hang before girthing up. If they are hanging too far back chances are that the girth will pull them forward and the saddle will ride up on the shoulder.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/T5Oez5oixLs
Author of ‘Suffering in Silence – The Saddle fit Link to Physical and Psychological Trauma in Horses’ (2013) Jochen Schleese teaches riders and professionals to recognize saddle fit issues in Saddlefit 4 Life® lectures and seminars. We help you find answers in a personal 80 point Saddle Fit Diagnostic Evaluation.
1-800-225-2242 www.Saddlefit4life.com