When it comes to horses, I don’t like easy projects. I love big challenges, if I feel the talent is there. I love structuring the horse’s work and closely monitoring his physical reaction to that work, to bring out that talent. That is the secret to my success with Parzival (by Jazz, out of Fidora by Ulft). I train my own body and have felt for myself how important a structured, monitored program is for an athlete.
As part of this overall fitness program, I ride my horses with a heart monitor, so I can make sure they are achieving the goals of that day’s work without overdoing it. One day it allowed me to catch a problem with Parzival’s heart. Soon after that, he was diagnosed with cardiac arrhythmia. Thankfully, we were able to provide him with the medical treatment he needed to recover from his heart condition. He was operated on and now he is very fit again. Because he is a real fighter, just six weeks after his condition was treated he won medals at the Europeans. He is so special. Parzival also was an incredibly difficult horse to train, requiring immense mental toughness on my part.
Parzival helped crystallize in my mind how integral physical and mental fitness are to achieving success, and this is the story of how I dealt with those demands. But I believe that anyone, even if your horse isn’t competing at Grand Prix with a heart problem, will benefit from a structured, monitored plan for mental and physical fitness.
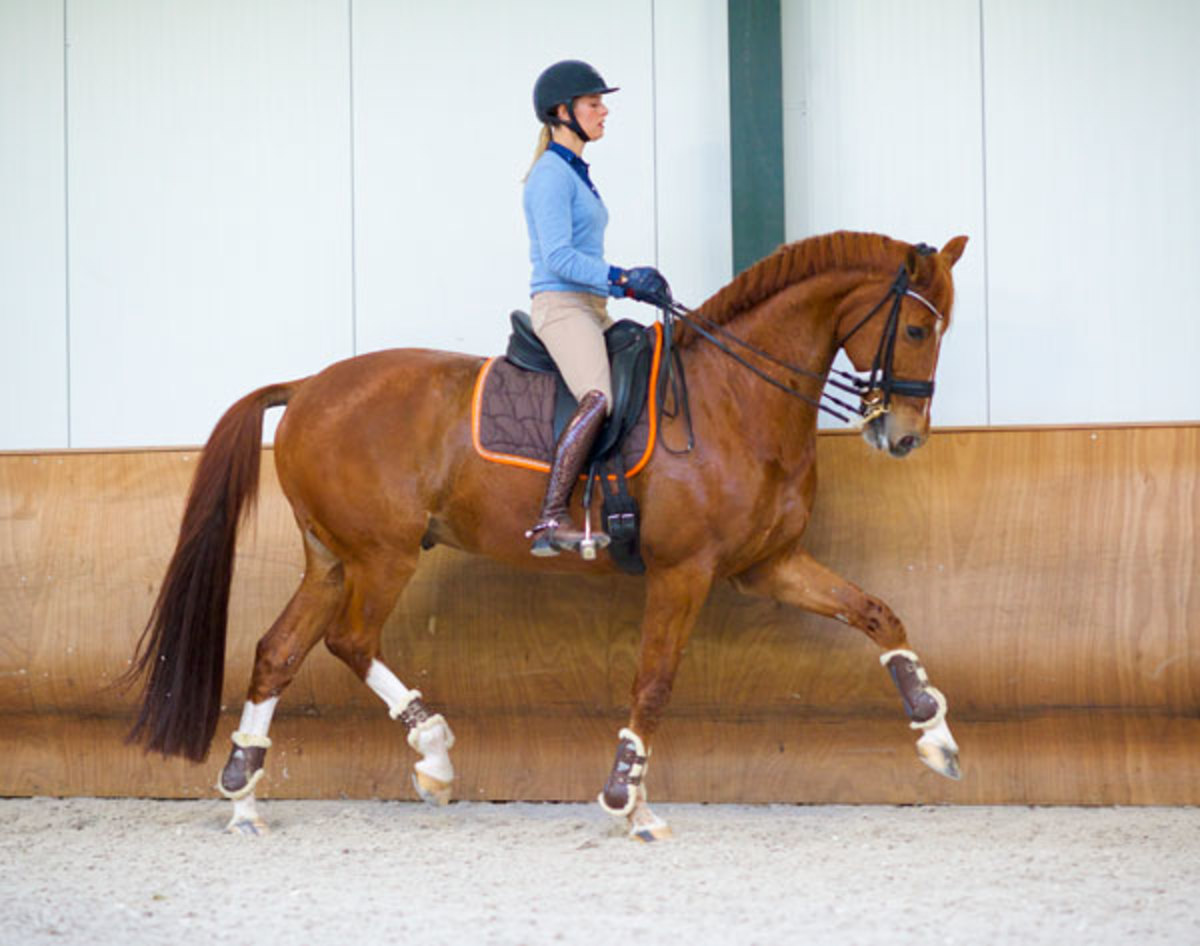


Equine Fitness
Any Grand Prix horse needs to be fit, so with the help of the heart monitor, I do interval training with Parzival. I think it is the best way to train. Just 40 minutes of easy work is not training, so I make sure that he reaches a certain heart rate three times during his training session. The level changes every day, based on his program, but I write everything down in a training diary to make sure we are on track. I find that it is a good way to know my horse. For example, Parzival’s heart rate is highest during the one tempis. The pirouette is also hard, and his beats per minute actually go down during piaffe and passage.
When Parzival does less hard work, I train longer; with the harder work, we have a shorter training session. I might be on the horse for an hour and a half—that includes 20 minutes of walk and 20 minutes of cool down. I always start with a walk through the woods, and, when possible, I warm up on the track. Arena work might be about 20 percent of the entire session, and I like to incorporate work with poles and small jumps.
To make an athlete out of my horse, I work to build up the right muscles in the right places. Therefore, I need to be able to control, isolate and flex every single part of his body. The more advanced the horse, the more balanced he is and the more I can play with the exercises. With the young horses, I want to make sure they stay in a comfortable place that they can manage.
The fitter the horse is, the easier—and more fun—it is for him to do the work. I don’t always train the difficult things. Imagine if you went to work every day and all day long, you had to do something you didn’t like or couldn’t do. You would hate it. So also train the things the horse finds easy and fun, especially at the end of a session.
If Parzival has a hard day, I make sure to work him the next day so he does not stiffen up. However, I still use the heart monitor to make sure that when I work him longer, I do so with a lower intensity.
My horses also go out in the paddock half the day. The goal is to keep my horses happy. I live by the rule that they may break a leg in the paddock, but if I keep them in the stable all the time they will certainly break their brains.

Human Fitness
I am passionate about my own fitness program as well. I have even created an online training center (adelindetrainingcenter.nl) with my partner, Sjaark van der Lei, and my fitness trainer, Tjalling van den Berg. Fitness is an important aspect of dressage because nowadays the horses are all of high quality, and the riders are getting better and better.
Talent is not where you’re going to make the difference in competition anymore. If you want to win, you need to have the full package. You need to be mentally and physically at the top. That’s where all the little percentages can be gained in competition.
Even if you don’t compete at that level (or any level), you owe it to your horse to be fit. You don’t want to be the weakest link. We expect our horses to be in top shape every day of the year, so if we’re not, that’s not fair. You have a long list of things you do for your horse, but what about for yourself: nothing? That’s not right.
Nutrition is part of the equation. Over time, I have changed how I eat. I used to eat bread and jam in the mornings, but then my nutritionist had me write down everything I ate for a week. Seeing everything written down like that, you start to think twice before picking up the chocolate! So now I am more likely to skip it, which is good. I can eat anything, but of course I have to be aware that I’m not eating pizza seven days a week. The whole summer I was focusing on getting a lot of vitamins and eating lots of fruit. I’ve never been into alcohol or smoking, so that helps, too.
Treating myself as an athlete has changed me tremendously. I have experienced big changes. I have started to be aware of my own body and what muscles I use and how I use them. This awareness is very important. When, for example, I tell some students to relax their upper legs and just sit, they tell me how much easier it is to ride. I often ask myself: Where do I have tension? Where do I relax? How do I get this position without tensing up?
Your body needs to be as quiet as it can be so the horse can pick up the small signals. For this, you need a certain tension in your body, a core stability but not tightness. Both horse and rider need relaxation first, but it’s not your end goal: You need the perfect tension in the right muscles.
When you train your own body, you realize how training affects your horse’s body. You realize that muscles cannot keep going on forever. Riders often make this mistake, especially when an exercise isn’t going well. They keep going with it, and wonder why it gets worse and worse. People don’t seem to realize that the horse is getting tired.
When I came onto the Olympic squad, I thought that I really had to do something to increase my conditioning, not just for myself but for my horse. So I started working with Tjalling, whois about 1.5 hours away from me. He asked me to come every Wednesday from 11:30 a.m. to 1:30 p.m. This was hard because of my commitments, but he said, “Think about your priorities!”
Tjalling, who used to train the Dutch gymnastics team, is not one to mess with. The only answer he accepts is, “Yes, sir!” It is definitely worth the effort. He’s a tough man but also a generous one who is utterly passionate about what he does. When I asked him what he wanted in return for his help, he said, “If you win a gold medal in London, I want a thank you. If not, I don’t want anything.”
My training with Tjalling consists of boxing, ballet, running, work on the trampoline or balance beam, core stability on the ball and/or balancing blindfolded. I’ve done so many weird things. In two years of training with him, one week has never been the same as another. He constantly gets me out of my comfort zone to see how I respond. You see it is only when you are out of your comfort zone that you start training. If you always do what you did, you always get what you got!
Tjalling provides 20 coaches to take me through the different exercises. There is also a mental coach at the gym, John van Apeldoorn, who is there for the whole two hours of my training session. He walks around, monitoring all the athletes he works with at the facility.
John doesn’t sit down and talk about how I feel before a competition. He puts me in situations as I train and asks me how I feel. For example, I might be doing my boxing, and if he sees me getting my breathing up or stiffening, he makes me aware of it and asks how I feel at that moment.
This is really important. When you are riding, you don’t really have time to think about your own balance or your own breathing. If you look at riders, half of them are not breathing or not breathing correctly and breathing way too high. They breathe in and then forget to breathe out. That causes a rider to stiffen up in her shoulders, which causes the horse to get stronger, and the rider, in response, stiffens her legs. And on and on. Breathing deep and low gets your center of gravity low and helps you with your balance. Then it is easier for your horse to carry you.
When you box, you become aware of your breathing; you notice when it gets too high and can change it. You can get your breathing relaxed and more grounded into your core and, hence, you become more stable. Tai Chi, yoga and Pilates are great for that as well. If you want your horse to balance, you have to learn to balance yourself.
The awareness needs to extend beyond just your breathing to your whole body. It’s important to understand what the horse is experiencing, trying to do piaffe, passage and pirouettes with an unbalanced rider on his back.
When I did a pirouette at the ballet bar, if I leaned a little to the left or right, I totally lost my balance. Now, when I am on a horse, I really think about being centered with my upper body, not leaning to one side so the horse would have to correct that imbalance.
I love boxing because it has so much in common with riding—the coordination, the balance, the breathing, the quickness of reactions, being able to relax again straight afterward and the mental part of it. You start to realize you can do more than you think you can. That is the goal: to meet the challenge.
I love what I do, and it gives me energy. It is why I am able to start at 6:00 a.m. Though I used to teach as late as 11:00 p.m., I have also learned I need my rest. I always remind myself that rest is one of the most important parts of training.
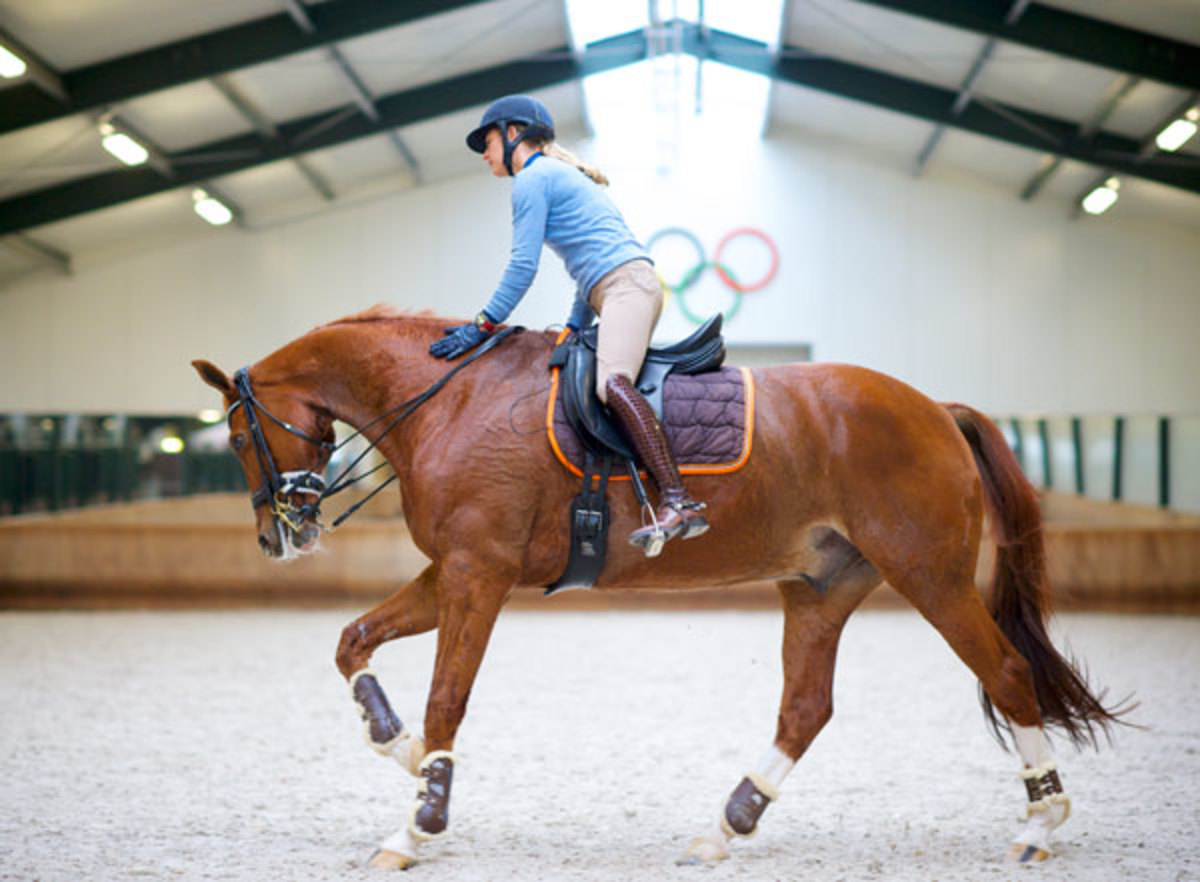


Parzival: The Mad Genius
Though we are now succeeding at the top level and have gone to the Olympic Games, Parzival has been a major challenge who pointed out to me how mentally strong a rider needs to be when training a difficult horse.
Just before I got Parzival, I was at home (having spent a year in Canada) when his owner turned up on my doorstop. He told me that Parzival put four people in the hospital and, therefore, he wanted to sell him. Parzival was then five, a stallion and could walk, trot, canter and execute a single flying change.
I had nothing else to do so I went and had a look at him. It took me 20 minutes to get on. He was so sensitive and spinning and within two seconds I was at the other end of the arena and then back again. His tongue was sticking out and I had no control.
When a buyer came to look, I was already on. They watched for 15 minutes and they didn’t want to try riding him themselves.
The first three years of his life he was in a paddock on his own, with no humans and no other horses to see, and I think this caused a lot of his problems. I told the owner I would ride him for a bit to get him a little more normal so he could be sold.
While riding, I would get three super strides and I would think wow, but then he would be crazy again. However, I felt the potential. People would tell me I was going to be killed but I loved the challenge.
I was an amateur at the time, and I think that was to my advantage. All of the riders who had tried to work with him before me were professionals. Difficult horses like Parzival need a lot of time, and with me he wasn’t my number 10 horse. He was number one, and I believe that really counts. Because of that, we formed a great partnership.
If you give your horse your full attention, he will give you his full attention back. I did (and still do) everything for Parzival myself: feeding, tacking up, etc.
I had to take Parzival out to many different places so he could see a lot. On one outing, he went crazy and I broke my arm in two places trying to stay on. I still have two metal plates and 13 pins in my arm holding it together.
During my recovery, no one else wanted to ride him, so he sat in the field and was gelded. I started with him again when my arm was OK.
The spookiness stayed for so so long, but now, knock on wood, he is good. But you have to have a lot of patience and you have to really believe. The process really proved to me that you have to be mentally strong to stay on your path.
Three Exercises for Rider Mental and Physical Fitness
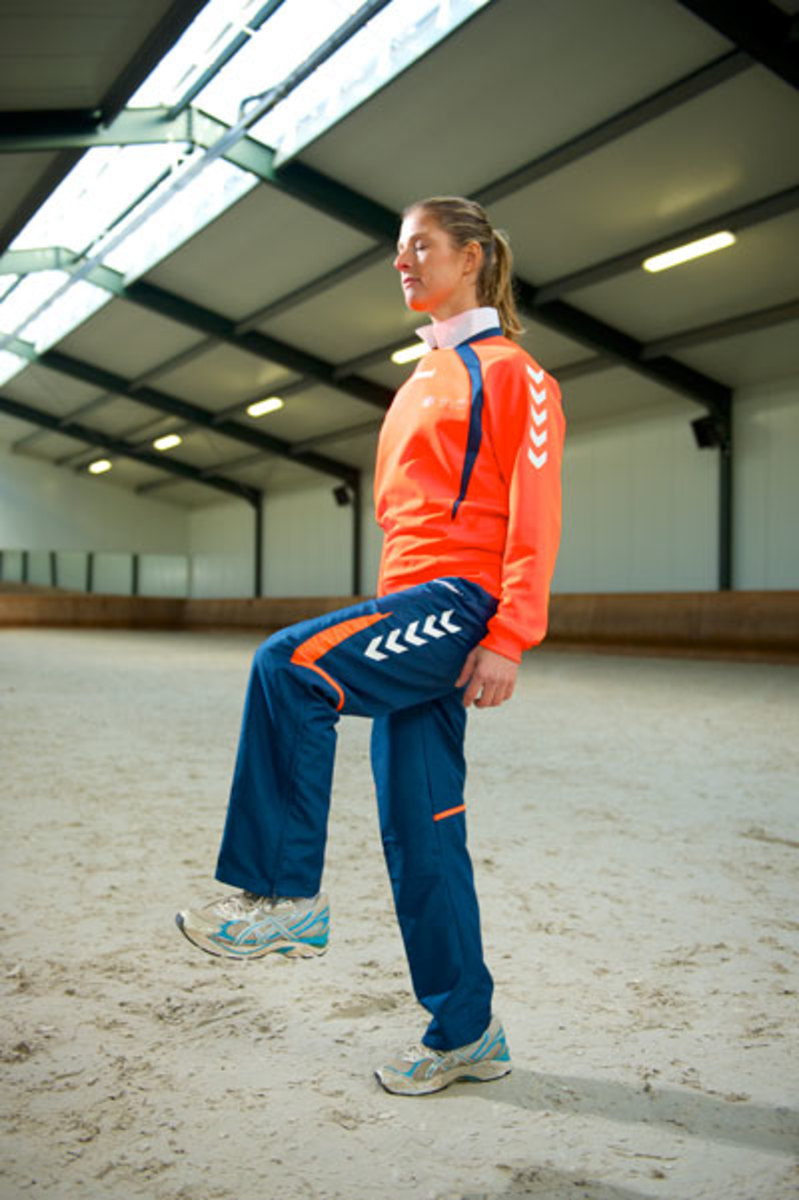
1. Balance: Your horse needs to balance on one foot in certain movements, so you owe it to him to improve your own balance. When I brush my teeth, I stand on one foot, and I encourage riders to practice this test of balance. This is a great way to start thinking about how your balance is as a rider.
Once you feel comfortable standing on one foot, test your balance by asking a friend to lightly push you in varying directions. If that gets easy enough, increase the difficulty by trying it with your eyes closed.
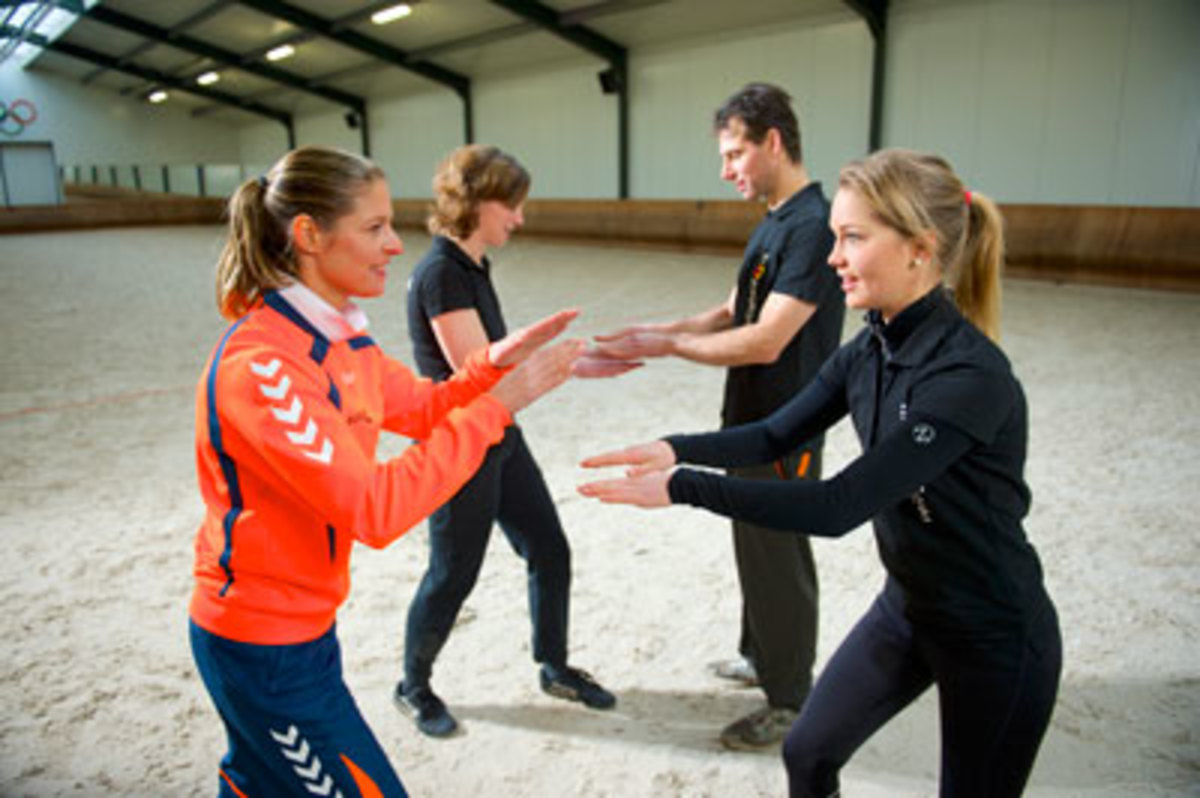


2. Reaction: Dressage is about a partnership and responding to each other’s decisions and movements. Improve your reaction time by facing a friend with both of your hands out, palms down, fingers touching. Take turns trying to slap the top of each other’s hand before you or she can pull them away.
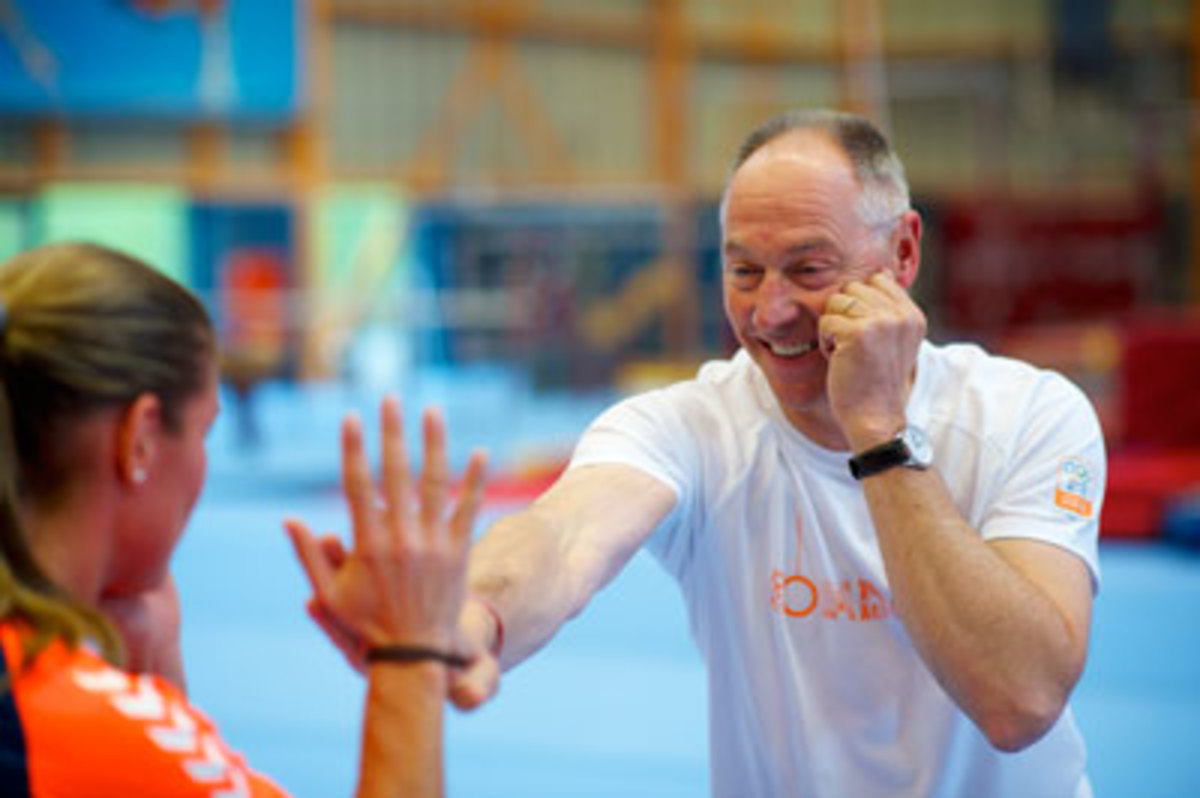

3. Coordination: A good dressage rider comes up with different combinations of movements and exercises to keep her horse from anticipating his work. This boxing exercise challenges a person in the same way.
Have your friend put his hands up, palms facing out. Punch his palms as fast as possible while he moves them around. This requires you to quickly respond to the patterns he chooses.

Adelinde Cornelissenis a Dutch Grand Prix competitor and trainer. Aboard Parzival, she won individual silver and team bronze at the 2012 Olympic Games in London. The pair has represented their country in multiple international-level events, including the 2011 World Cup Final in Leipzig, where they won individual gold and team bronze (adelindecornelissen.nl).